
The year 2020 will witness large-scale commercial use of 5G and constantly emerging new 5G services. New requirements including localized applications (data restricted in the campus), distributed contents (CDN deployed at the edge) and edge-based computing (5GU moved down to the edge) have changed the traditional centralized deployment architecture of 4G core networks. Three-level distributed telecom cloud architecture (MEC, Edge DC and Core DC) has been widely recognized by operators and deployed level by level.
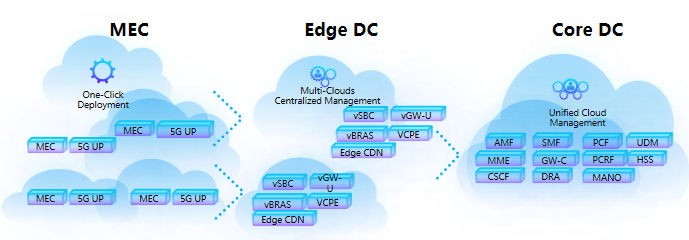
Figure 1 Three-Level Distributed DC
Different from traditional centralized telecom cloud, deploying distributed telecom cloud poses the following four new requirements for transport networks:
- DC resource pool-based scheduling, to achieve flexible deployment of virtual network elements across DCs or servers;
- Carrier-grade 99.999% reliability, to implement fast fault detection and restoration based on active/standby virtual machines (VMs) of VNF network elements;
- One-to-one mapping between IP networks and VNF network elements, to realize end-to-end orchestration from services to networks;
- The network must be capable of self-analysis and self-adjustment.
Based on years of experience in network construction, ZTE has established complete telecom cloud NFVI solutions and built a profound technological foundation in the telecom cloud market. Facing the challenges, ZTE proposes the solution of building a “distributed, carrier-grade, intelligent” 5G telecom cloud network to meet the 5G service development requirements and help operators create a new future.

Figure 2 Architecture of Distributed 5G Telecom Cloud Network
The key technologies of ZTE 5G telecom cloud network are shown below:
I. Rich and flexible routing protocols for resource pool-based scheduling
ZTE telecom cloud solution supports the new “Floating, Distributed, Dynamic Routing (FDDR)” technology that is capable of distributing and learning millions of routing entries. Take vGW as an example, it can meet the service requirements of massive mobile phones. For such a huge routing capacity, traditional static route configuration cannot meet the requirement. The system must support dynamic routing protocols, such as BGP and OSPF. At the same time, dynamic routing protocols also match the innate “dynamic migration” feature of the VM of the vGW. The route configuration policies float with the migration of the VM, so it also has the “floating” feature.
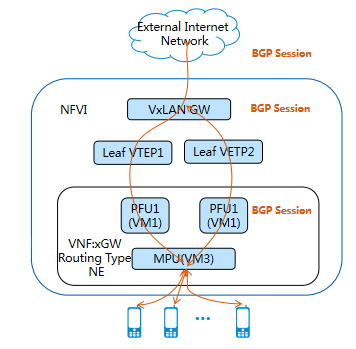
Figure 3 FDDR Function Diagram
II. Massive BFD Sessions for Fast Fault Detection and Carrier-Grade 99.999% Reliability
Different from IT cloud networks, telecom cloud networks are required to have very high reliability and support ms-level fault restoration. In a virtual telecom cloud, take xGW as an example, the functional network element is generally deployed on two or more VMs, and the data traffic load is shared by the two (or more) VMs. The network must support detection mechanism and link restoration mechanism in case of VM failure.
ZTE telecom cloud IP network products support Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) function. BFD sessions are configured between the ZXR10 M6000-S (as the DC VxLAN egress gateway) and the vGW VM. Once the active VM fails, the DCGW detects the link failure rapidly and switches the traffic to the standby VM. If the failed active VM is restored, the DCGW re-negotiates the BFD session and switches the traffic back. During the whole process, the services are not interrupted and the users do not perceive the switching.
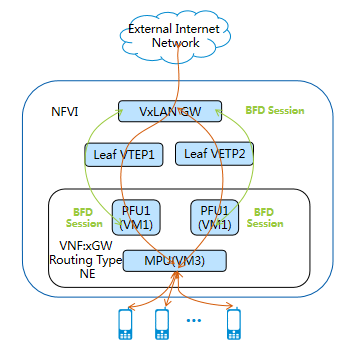
Figure 4 BFD Function Diagram
III. Unified Orchestration & Management of Services and Networks Achieve Real “Network Adjustment with Cloud”
ZTE telecom cloud solution consist of orchestrator, TECS Openstack unified cloud management platform, ZENIC vDC controller, Spine-Leaf switch, SDN gateway and other components (L4-L7 services: FW and LB, etc.). The cloud management platform is responsible for computing, storage and management of virtual network elements and unified scheduling and allocation of resources. The SDN controller is responsible for the configuration of end-to-end routing protocols for IP networks. Based on the network element function requirements provided by the cloud platform and the network resources provided by the controller, the orchestrator performs one-to-one mapping between service network elements and IP networks, end-to-end orchestration and automatic deployment of routing protocols , so as to realize network adjustment with cloud.
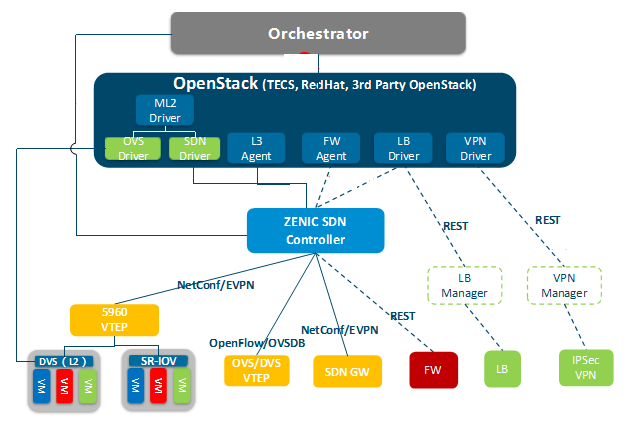
Figure 5 ZTE Cloud and Network Synergy Solution
IV. Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Achieve Network Self-Learning and Self-Healing
The telecom cloud network must be capable of self-analysis and self-adjustment to meet the operators’ requirements for automation and intelligence. For example,in order of improving the utilization rate of the operator’s network while meeting the users’ service requirements, the network judges the busy and idle hours by collecting statistics on the bandwidth requirements of each mobile phone users and makes intelligent adjustment & adaptation for network bandwidth.
ZTE SDN solution provides autonomous network closed-loop feedback and self-adaptation function with the data analysis system based on TAP as a Service (TAAS) of Openstack. The ANS navigator obtains the statistical information of the IP layer, such as real-time traffic collection through the mirror aggregation switch, and collects statistical information of the system such as logs and alarms through the controller and the EMS. Based on correlative and comparative analysis of the information, it makes intelligent analysis and adjustment for network congestions and root cause analysis for faults to realize network self-learning and self-management.
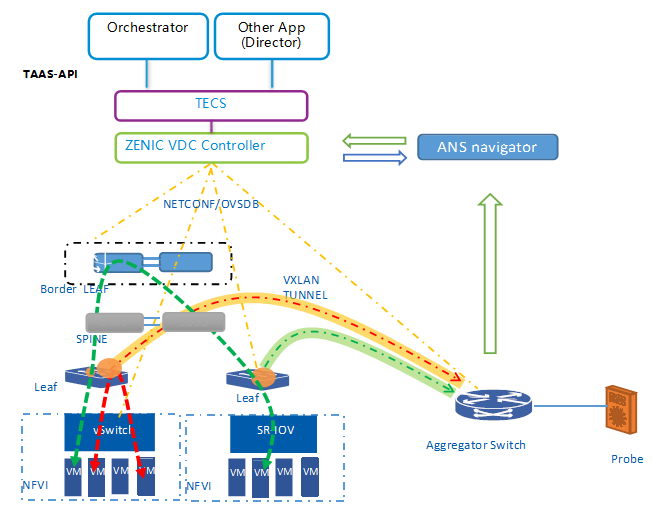
Figure 6 TAAS Traffic Analysis and Network Self-Learning
Based on the key technologies of 5G telecom cloud solution shown above, ZTE has successfully deployed more than 500 commercial projects and POC projects using the ZXR10 M6000-S as DC gateway egress router, the ZXR10 9900 as the Spine, the ZXR10 5960 as the Leaf and the ZENIC vDC as the SDN controller. In the future, ZTE will intensify the cooperation with global operators to build telecom cloud networks together and create a new future of 5G.

